And Contribute to Hyperglycemia
Introduction to Excessive Blood Sugar Ranges [Hyperglycemia]
Prior to now, I’ve posted articles on impaired blood sugar ranges that trigger a situation referred to as Diabetes. Right now, on this article we’re going to find out how the blood sugar ranges are regulated by eight such organs and what causes these ranges to rise [or fall] and the methods to handle it.
Hyperglycemia, generally acknowledged as excessive blood sugar, is a situation that happens when there may be an extreme quantity of glucose circulating within the bloodstream. This situation is usually related to diabetes, however it can be influenced by varied different elements and well being circumstances.
Sustaining balanced blood sugar ranges is essential for total well being, as glucose is a main power supply for the physique’s cells. Persistent hyperglycemia can result in a myriad of well being problems, together with cardiovascular ailments, nerve injury, kidney failure, and imaginative and prescient issues.
The regulation of blood sugar ranges is a posh course of that includes a number of organs working in concord. Disruption within the perform of any of those organs can result in hyperglycemia.
That are the organs influencing blood sugar ranges?
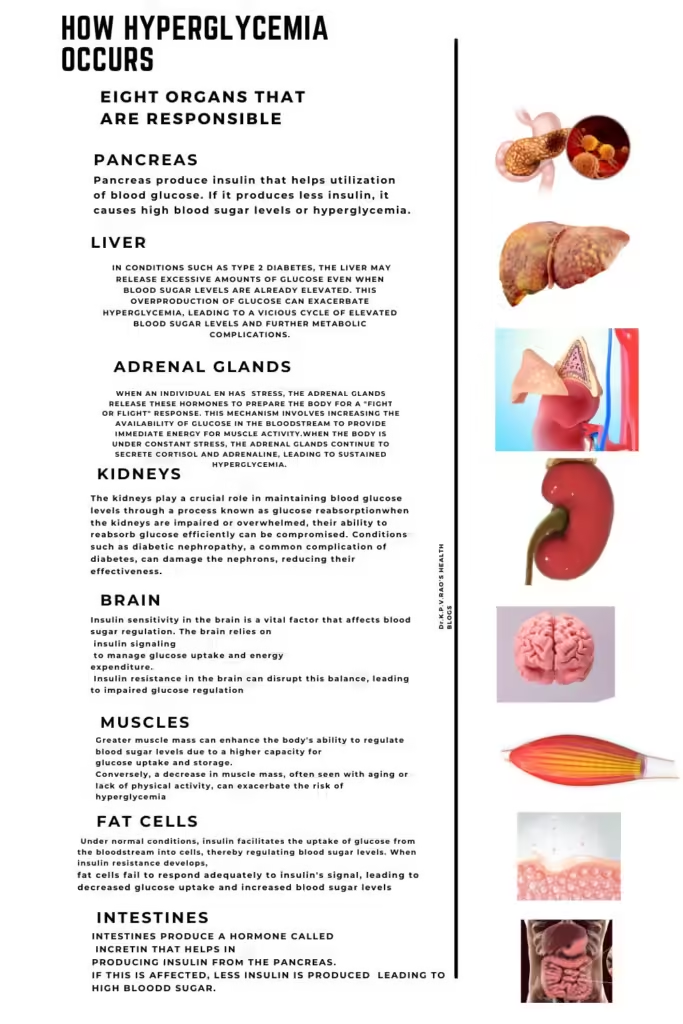
The pancreas, liver, muscle tissues, adipose tissue, kidneys, mind, intestines, and pores and skin all contribute to the fragile steadiness of glucose within the physique. Every organ performs a novel function in both the manufacturing, storage, or utilization of glucose, and their coordinated efforts are important to stop hyperglycemia.
As an illustration, the pancreas produces insulin, a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose by cells. The liver shops glucose within the type of glycogen and releases it into the bloodstream as wanted. Muscle tissues and adipose tissues additionally retailer and make the most of glucose, taking part in vital roles in sustaining blood sugar ranges. The kidneys filter the blood, reabsorbing glucose and stopping its loss by urine. The mind, intestines, and pores and skin are additionally concerned in varied metabolic processes that affect glucose ranges.
Why is studying about these eight organs necessary?
Understanding how these eight organs affect blood sugar ranges offers priceless insights into the multifaceted nature of hyperglycemia.
It highlights the significance of a holistic strategy to well being, the place the performance of every organ have to be thought of to stop and handle excessive blood sugar.
On this weblog publish, we’ll be taught the particular roles of those organs and the way their dysfunction can contribute to hyperglycemia, providing a whole information of the interconnected mechanisms regulating blood sugar ranges.
As this text is kind of exhaustive, let’s break up it into two elements. Within the first half we be taught concerning the first 4 main organs, particularly the pancreas, liver, mind, and the kidney’s function in regulating blood sugar ranges and within the subsequent half, we’ll find out how adrenal glands, fatty tissues, our muscle tissues, and the intestines do it. So, let’s begin-
The Pancreas: Insulin Manufacturing and Launch
The pancreas performs a vital function in sustaining blood sugar homeostasis by its manufacturing and launch of insulin. This important organ accommodates clusters of cells often called the islets of Langerhans, which home beta cells answerable for insulin secretion. Insulin is a hormone that facilitates the uptake of glucose by the physique’s cells, permitting them to make the most of glucose as a supply of power. When meals is ingested, glucose ranges within the bloodstream rise, prompting the pancreas to launch insulin. This launch alerts cells within the liver, muscle, and fats tissue to soak up glucose, thereby lowering the focus of glucose within the blood.
Nevertheless, when the pancreas fails to supply ample quantities of insulin or when the physique’s cells turn into proof against insulin, hyperglycemia can happen.
Hyperglycemia, outlined as elevated blood glucose ranges, may result from a number of pancreatic dysfunctions. One widespread subject is Sort 1 diabetes, an autoimmune situation the place our immune system mistakenly assaults and destroys insulin-producing beta cells. Consequently, in folks with Sort 1 diabetes, one should depend on exterior insulin administration to handle their blood sugar ranges.
One other vital situation is Sort 2 diabetes, the place the pancreas produces insulin, however the physique’s cells turn into proof against its results.
Initially, the pancreas compensates by producing extra insulin, however over time, it could turn into overworked and fail to keep up the mandatory insulin ranges. This insulin resistance prevents cells from absorbing glucose effectively, resulting in persistent hyperglycemia.
Continual hyperglycemia can have detrimental results on varied organs and techniques, emphasizing the pancreas’s essential function in regulating blood sugar ranges.
Pancreas additionally produce glucagon within the alpha cells of the islet of Langerhans. This hormone acts on liver cells to launch glucose saved as glycogen in liver cells [explained below].
To summarize, the pancreas’s means to supply and launch insulin is the fundamental requirement to stop hyperglycemia. Adjustments on this course of, whether or not as a consequence of autoimmune destruction, insulin resistance, or some other elements, can considerably impression blood sugar regulation and contribute to the event of diabetes and associated problems.
Helpful Article: How Insulin and Glucagon regulate Blood Sigar
The Liver: Glucose Storage and Launch
The liver performs a pivotal function in sustaining blood sugar ranges by two main processes:
- Glycogen storage and
- Glucose launch.
Glycogen, a polymer of glucose, is saved within the liver and acts as a reserve of power that may be mobilized when the physique requires further glucose. This storage mechanism is essential for making certain a gentle provide of glucose, notably between meals and through bodily exertion.
So, how does the liver regulate blood sugar ranges?
When blood sugar ranges drop, the liver responds by breaking down glycogen into glucose by a course of often called glycogenolysis. This glucose is then launched into the bloodstream to offer a fast supply of power. Glycogenolysis is a speedy response mechanism, making certain that the physique can preserve homeostasis and meet its power calls for promptly. The hormone glucagon from the pancreas helps on this course of.
Along with glycogenolysis, the liver can even produce glucose from non-carbohydrate sources by a course of referred to as gluconeogenesis. This includes changing amino acids, lactate, and glycerol into glucose, which may then be launched into the bloodstream.
Gluconeogenesis is especially necessary throughout extended fasting or intense bodily exercise, the place glycogen reserves is likely to be depleted.
Nevertheless, the liver’s means to launch glucose can turn into a contributing issue to hyperglycemia when it’s dysregulated. In circumstances corresponding to kind 2 diabetes, the liver could launch extreme quantities of glucose even when blood sugar ranges are already elevated. This overproduction of glucose can worsen hyperglycemia, resulting in a vicious cycle of elevated blood sugar ranges and additional metabolic problems.
Due to this fact, understanding the liver’s twin function in glucose storage and launch is important for managing blood sugar ranges successfully. By regulating these processes, it’s attainable to mitigate the chance of hyperglycemia and preserve total metabolic well being.
The Kidneys: Glucose Reabsorption
The kidneys play an necessary function in sustaining blood glucose ranges by a course of often called glucose reabsorption. This intricate process begins within the nephrons, the practical items of the kidneys. As blood flows by the glomeruli, the preliminary filtering items, glucose is filtered out of the bloodstream together with different substances.
Nevertheless, below regular physiological circumstances, the vast majority of this glucose is reabsorbed again into the bloodstream by specialised transporters within the renal tubules. This reabsorption course of ensures that glucose just isn’t misplaced within the urine and is offered for the physique’s power wants.
How do the kidneys regulate blood sugar ranges?
The first mechanism of glucose reabsorption includes sodium-glucose cotransporters (SGLT) situated within the proximal convoluted tubule of the nephron. These transporters facilitate the motion of glucose from the filtrate again into the blood. Particularly, SGLT2 reabsorbs round 90% of the glucose, whereas SGLT1 accounts for the remaining 10%. This extremely environment friendly system is essential for sustaining regular blood glucose ranges.
Nevertheless, when the kidneys are impaired or overwhelmed, their means to reabsorb glucose effectively will be compromised. Situations corresponding to diabetic nephropathy, a typical complication of diabetes, can injury the nephrons, lowering their effectiveness.
When the blood glucose ranges exceed the renal threshold, sometimes round 180 mg/dL, the transporters turn into saturated, and glucose begins to spill into the urine, a situation often called glucosuria. This extra glucose within the urine is a trademark of hyperglycemia and might result in additional problems if not managed correctly.
Furthermore, sure drugs that inhibit SGLT2, often called SGLT2 inhibitors, are used therapeutically to handle hyperglycemia by selling the excretion of glucose within the urine. Whereas efficient, these drugs spotlight the fragile steadiness the kidneys should preserve in glucose reabsorption to keep away from contributing to hyperglycemia.
The Mind: Urge for food Regulation and Insulin Sensitivity
The mind performs a vital function within the regulation of urge for food and insulin sensitivity, considerably influencing blood sugar ranges. The hypothalamus, a vital area of the mind, is answerable for processing alerts associated to starvation and satiety.
When the physique senses a drop in blood glucose ranges, the hypothalamus triggers the discharge of hormones that promote emotions of starvation, prompting meals consumption. Conversely, when blood glucose ranges rise, the hypothalamus releases hormones that sign satiety, serving to to regulate meals consumption.
Insulin sensitivity within the mind is an important issue that impacts blood sugar regulation. The mind depends on insulin signaling to handle glucose uptake and power expenditure. Insulin resistance within the mind can disrupt this steadiness, resulting in impaired glucose regulation.
When the mind turns into much less aware of insulin, it can lead to elevated urge for food and overeating, additional contributing to hyperglycemia. This insulin resistance can even impair the mind’s means to control peripheral glucose metabolism, selling excessive blood sugar ranges.
Moreover, the mind’s communication with different organs by the autonomic nervous system is important for sustaining glucose homeostasis.
Dysregulation in these neural pathways can result in improper signaling between the mind and the pancreas, liver, and muscle tissues, additional contributing to hyperglycemia.
These neural dysfunctions can disrupt the fragile steadiness required for optimum blood sugar management, making the administration of hyperglycemia more difficult.
To summarize, understanding the mind’s function in urge for food regulation and insulin sensitivity is essential for creating efficient methods to fight hyperglycemia. By addressing neural mechanisms and enhancing insulin sensitivity within the mind, it could be attainable to reinforce total glucose regulation and cut back the chance of long-term problems related to excessive blood sugar ranges. This highlights the significance of contemplating the mind’s affect when creating complete approaches to managing hyperglycemia.
To be concluded….
In my subsequent article we’ll focus on the remaining 4 organs that regulate blood sugar ranges. You may choose to get notification by subscribing to the notification by clicking on the bell icon within the article.
Adios.